Top Ethernet Connectors: Choosing the Best for Your Network Needs
When building or upgrading a network, one of the most critical components to consider is the selection of ethernet connectors. These small but essential devices serve as the backbone of wired communication systems, enabling devices to communicate efficiently and reliably. With the vast array of options available on the market, choosing the right ethernet connectors can significantly influence the performance, speed, and stability of your network.
Understanding the different types of ethernet connectors and their specific applications is paramount for any network administrator or technology enthusiast. Whether you're setting up a simple home network or managing a complex corporate infrastructure, the correct connector can enhance your network’s throughput and minimize data loss. Factors such as compatibility with existing cabling, environment considerations, and future scalability should also play a vital role in your decision-making process. This guide aims to illuminate the various types of ethernet connectors, helping you navigate the options to find the best fit for your unique network needs.

Understanding Ethernet Connectors: Types and Uses
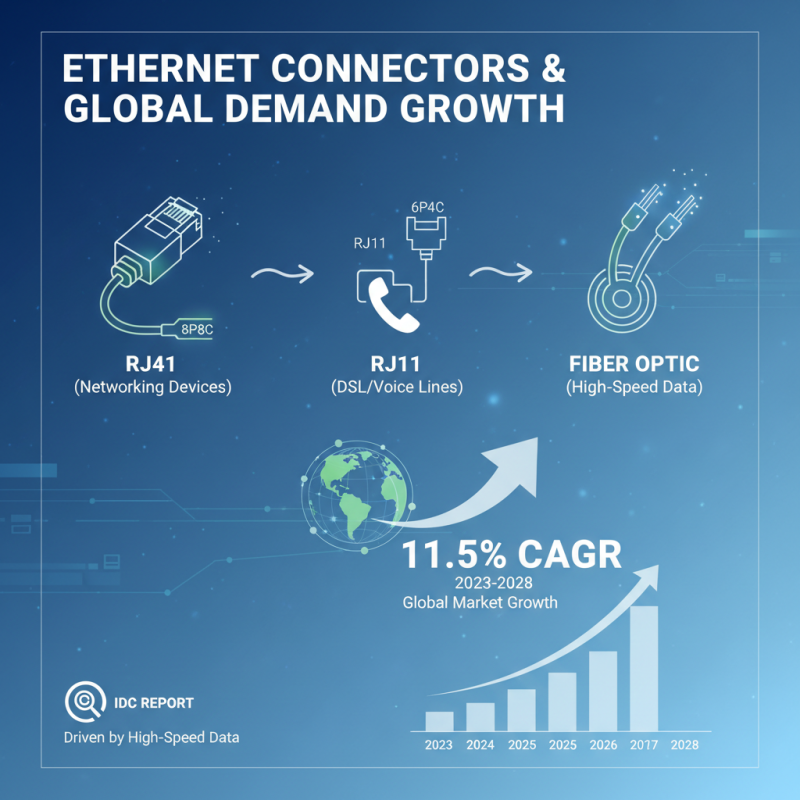
Ethernet connectors play a crucial role in networking, facilitating the connection between devices and ensuring effective communication within a network. The most common types of Ethernet connectors include RJ45, RJ11, and fiber optic connectors, each catering to different networking needs. According to a recent report by the International Data Corporation (IDC), the global demand for Ethernet connection solutions is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth can be attributed to the increasing need for high-speed data transmission in both residential and commercial sectors.
RJ45 connectors are primarily used for Ethernet networking in Local Area Networks (LAN) and are favored for their robust design and ability to support speeds up to 10 Gbps over short distances. Alternatively, fiber optic connectors, such as SC and LC, offer advantages when long-distance data transmission is required, as they provide higher bandwidth and lower attenuation. A report from MarketsandMarkets highlights that the fiber optics segment of Ethernet networking is expected to account for over 40% of the market share by 2025, driven by the rising adoption of cloud services and streaming applications that demand high throughput and low latency. Understanding the various types of Ethernet connectors and their appropriate applications is essential for optimizing network performance and meeting the growing data demands of modern technology.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing Ethernet Connectors
When selecting Ethernet connectors for your network, several key features should be considered to ensure optimal performance. Firstly, the category of the Ethernet connector is crucial, as it determines the bandwidth and maximum speed supported by your network. For example, connectors from higher categories like Cat6 or Cat6a enable faster data transmission and are suitable for high-speed applications, making them an ideal choice for modern networks that require substantial bandwidth.
Another important factor to consider is the connector type, which can range from RJ45 to more specialized options like LC or SC for fiber networks. Choosing the right connector type will depend on your specific network configuration and the type of devices being connected. Additionally, the material and design of the connector can affect durability and reliability. Look for connectors with robust construction to withstand physical wear and long-term use.
Tips: Always evaluate the installation environment, as moisture and dust can impact connector performance. If you're setting up in an industrial setting, consider connectors that offer weatherproofing or ruggedized designs. Also, ensure that the connectors are compatible with your existing cabling to prevent connectivity issues. Lastly, think about future scalability; opting for a slightly higher category may save you from needing replacements down the line.
Comparison of Common Ethernet Connector Types: RJ45, RJ11, and More
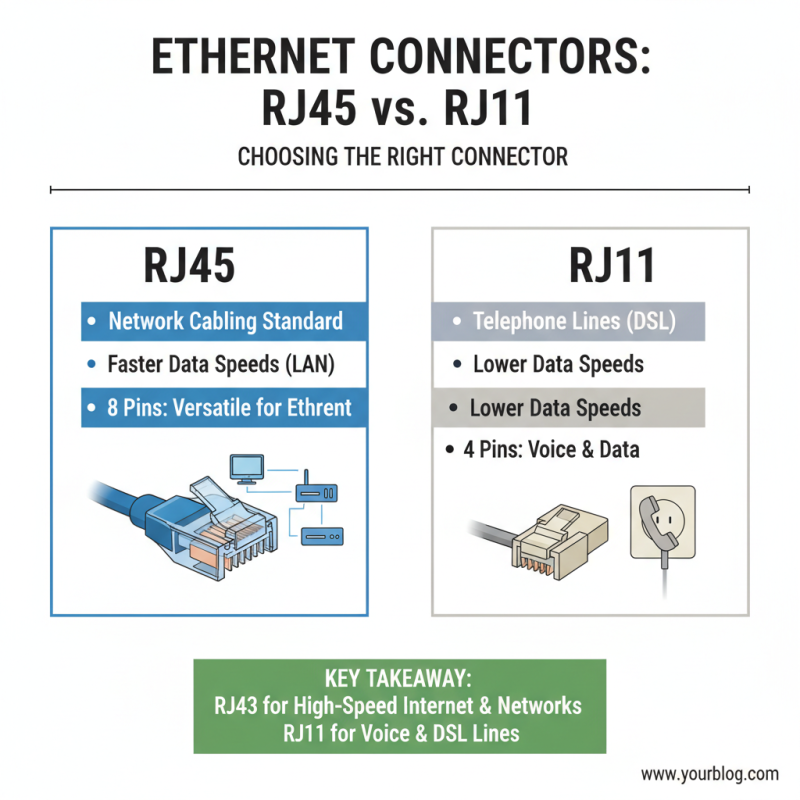
When selecting the right Ethernet connectors for your network, it's essential to understand the different types available, particularly RJ45 and RJ11, among others. RJ45 connectors are the standard for network cabling, commonly used in Ethernet networks to connect computers, routers, and switches. They support higher data speeds and allow for better performance in LAN settings, ensuring efficient data transfer and improved connectivity. RJ45 connectors feature eight pins, which enables them to support multiple network protocols, making them versatile for various networking needs.
On the other hand, RJ11 connectors are more commonly found in telephone systems. They have fewer pins—typically two or four—which limits their use primarily to telephone lines and some DSL connections. While RJ11 can occasionally be adapted for network purposes, it is not ideal for high-speed data transfer like RJ45. Understanding the differences in functionality and application between these connectors is critical for optimizing your network architecture and ensuring you select the connectors that best meet your requirements.
Installation Tips for Ethernet Connectors in Network Setup
When installing Ethernet connectors, ensuring a proper setup is crucial for achieving optimal network performance. Start by selecting the right connector type based on your cable specifications, such as Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a. Each category supports different speeds and bandwidths, so understanding your network requirements is essential. Once you've chosen the right connector, prepare your cables by stripping them back to the appropriate length and untwisting pairs carefully to maintain the integrity of the signal.
Next, follow the correct wiring scheme while connecting the colored wires to the Ethernet connector. It's important to keep the twists in the wire pairs as close to the connector as possible. This practice minimizes interference and enhances performance. After the wires are inserted, be sure to firmly crimp the connector to secure a solid connection. Always double-check your work with a cable tester to confirm that the connections are correctly established, which will help prevent network issues down the line. With proper installation techniques, you can ensure a reliable and high-speed network experience.
Top Ethernet Connectors: Choosing the Best for Your Network Needs
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Ethernet Connectors for Longevity
Maintaining and troubleshooting Ethernet connectors is essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your network. Regular inspection is a crucial first step in maintenance. Check for physical damage, such as bent pins or cracked housings, which can cause connection issues. Cleaning the connectors with a suitable electronic cleaner can also help remove dust and debris that may interfere with performance. It's advisable to use lint-free cloths or brushes specifically designed for electronic components to avoid scratching surfaces.
When problems arise, troubleshooting should begin with testing the connectors. Using a cable tester can help identify breaks or shorts in the wiring. If a connection is intermittent, reseating the connectors often resolves the issue, as connectors can sometimes become loose over time. Additionally, replace any connectors that show signs of wear or poor performance to prevent further disruptions. By following these maintenance and troubleshooting steps, you can maximize the efficiency of your Ethernet network and prolong the life of your connectors.
Top Ethernet Connectors: Choosing the Best for Your Network Needs
| Connector Type | Speed (Gbps) | Maximum Distance (m) | Applications | Maintenance Tips | Troubleshooting Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJ45 | 1 | 100 | Home and Office Networking | Keep connectors clean and dry. | Check cabling for bends or breaks. |
| LC | 10 | 300 | Data Centers, High-Density Applications | Inspect for dust and clean regularly. | Test with a loopback adapter if no connection. |
| SC | 10 | 500 | Telecommunications, Fiber Optic Networks | Perform visual inspection after long use. | Replace any damaged fiber cables. |
| MTP/MPO | 40-400 | 150 | High-Density Fiber Networks | Use proper cleaning tools to ensure performance. | Test each fiber strand for signal degradation. |
| SFP+ | 10-25 | 100 | Networking Equipment | Ensure proper insertion and seating in ports. | Check for compatibility with existing devices. |
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Ethernet Connectors Industry Insights from the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

How to Build a Reliable Network with Fiber Optic Connections
-

Understanding Fiber Optic Connections How They Revolutionize Internet Speed and Reliability
-
Top 10 Structured Cable Tips for Better Network Performance
-

Maximize Efficiency: The Top 7 Cable Management Tools to Enhance Workstation Productivity by 30%
-

How to Choose the Best Cable Management Tools for Your Workspace






